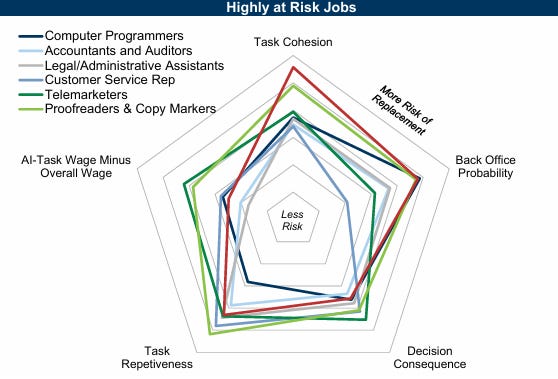
A.I.: Unemployment Can Spiral Higher Now
Unemployment in the Age of A.I.
Authored by GoldFix, ZH Edit
Summary: Structural Job Loss Without Recession
Structural unemployment in the U.S. economy is set to increase regardless of traditional business cycle conditions. Artificial intelligence and other labor-reducing technologies are being adopted at a pace that eliminates the need for sustained full employment. A recession is no longer required to trigger higher joblessness. Even in a period of moderate growth, unemployment will rise. If an actual downturn occurs, the pace of job loss may accelerate sharply. The economy is moving into a period where employment trends and corporate profitability no longer move in the same direction.
Assumptions
Two foundational assumptions guide this analysis:
Cost-cutting technologies are adopted more rapidly during economic slowdowns.
Historically, when revenue growth slows, companies turn to operational efficiency to preserve margins. Adoption of automation, outsourcing, and process optimization tends to accelerate during these phases. AI is the most recent and most powerful tool in that toolkit.Goldman expects 6–7% of workers displaced by AI
Goldman Sachs’ latest Global Economics Analyst piece assesses the labor market impact of generative AI, estimating moderate but measurable risks of job displacement. While long-term productivity gains are anticipated, near-term disruptions are emerging in AI-exposed industries. Read full story
AI qualifies as a scalable labor-reducing innovation.
Artificial intelligence improves productivity, reduces overhead, and in many functions, replaces human workers. The efficiency gains from AI adoption are measurable and compounding.
New Corroborating Observations
Recent data from the U.S. corporate sector and labor market reinforce these assumptions:
Profitability is improving despite labor market weakness.
According to FactSet, 82 percent of S&P 500 companies have exceeded Wall Street earnings estimates in Q2 2025. That is higher than the 1-, 5-, and 10-year averages of 77, 78, and 75 percent. Revenue beats are also significantly elevated, with 79 percent of firms surpassing forecasts. Earnings growth stands at 10.3 percent versus the same quarter last year.Labor market data shows deterioration, not strength.
The July jobs report revealed weaker-than-expected employment growth in Q2. Both May and June were revised downward, and July itself fell below consensus. Despite these weak labor figures, corporate earnings remained strong.
These points suggest that productivity gains are being achieved without corresponding increases in labor demand. Firms are maintaining or expanding profit margins while reducing reliance on human capital.
Implications
The traditional model that links GDP growth to job creation is no longer dependable. The current environment shows that output and profitability can improve even as employment conditions soften.
In the event of a recession: Unemployment Convexity
A weakening economy would provide a further incentive for firms to reduce costs. AI tools offer a ready path to achieve those reductions. As a result, job losses could rise quickly and with greater magnitude than seen in prior downturns. The usual rebound in hiring following a contraction may not materialize, since many roles will have been permanently automated.Even without a recession: Keeping Up With the Virtual Joneses
Competitive pressure alone will drive companies to cut labor costs. As firms adopt AI and similar technologies, those that delay adoption risk falling behind on cost structure. This creates a cascade of headcount reductions across sectors as firms seek to maintain parity.
Conclusion
The United States is entering a structural realignment of its labor market. The link between employment and corporate performance is unraveling. Unemployment is likely to increase in both...
Continues here
Free Posts To Your Mailbox