A Cost Model for Enrichment Services
From the TightSpreads Substack
"The Core Economics of Enrichment
Capital charges represent ~60-70% of the levelized cost for any new Western enrichment facility. This makes enrichment a high-fixed-cost, low-variable-cost business where the single most important variable is capacity utilization — not technology, not energy, not labor.
A mature Western enricher (Urenco-class) produces SWU at ~$135/SWU all-in. A new-build U.S. greenfield requires ~$201/SWU to break even. Russia produces at ~$33/SWU. These three numbers define the competitive boundaries of the global market.
At current spot pricing ($195/SWU per JPM 2026E), a mature plant earns a 31% gross margin, a U.S. greenfield barely breaks even, and Russia earns an 83% margin. Against historical contract prices ($98/SWU), no new Western capacity is viable.
The financing structure matters as much as the engineering. A DOE loan guarantee at ~2.5% versus 8% commercial financing reduces the LCOE by ~$76/SWU, nearly closing the entire gap between a greenfield ($201) and a mature plant ($135).
Why General Matter’s DUF6 Model Works" ..
The rest of this article is available to Premium Subscribers of the TightSpreads Substack.
It discusses:
- The Competitive Landscape
- Capital Costs
- Operating Costs
- Tails Management
- Three-Scenario Framework: Base case, US greenfield, Russian optimization
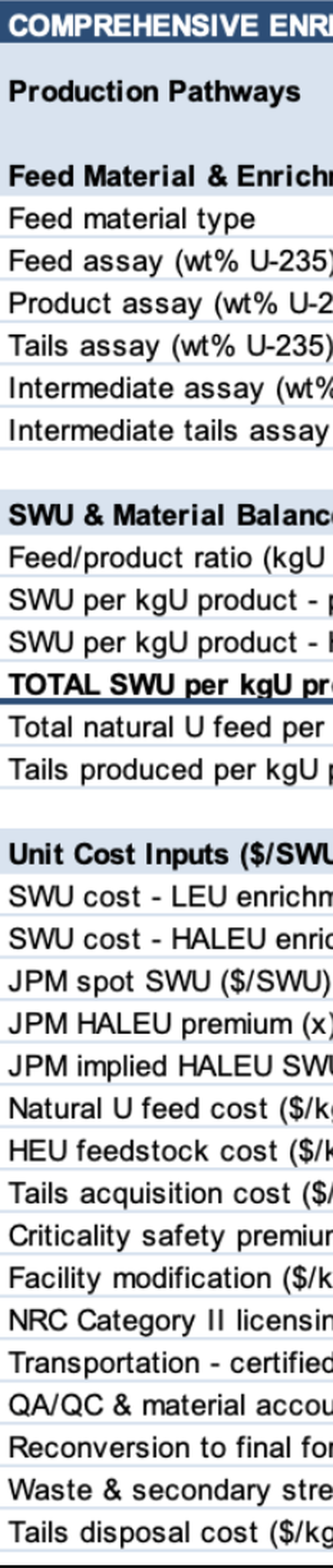
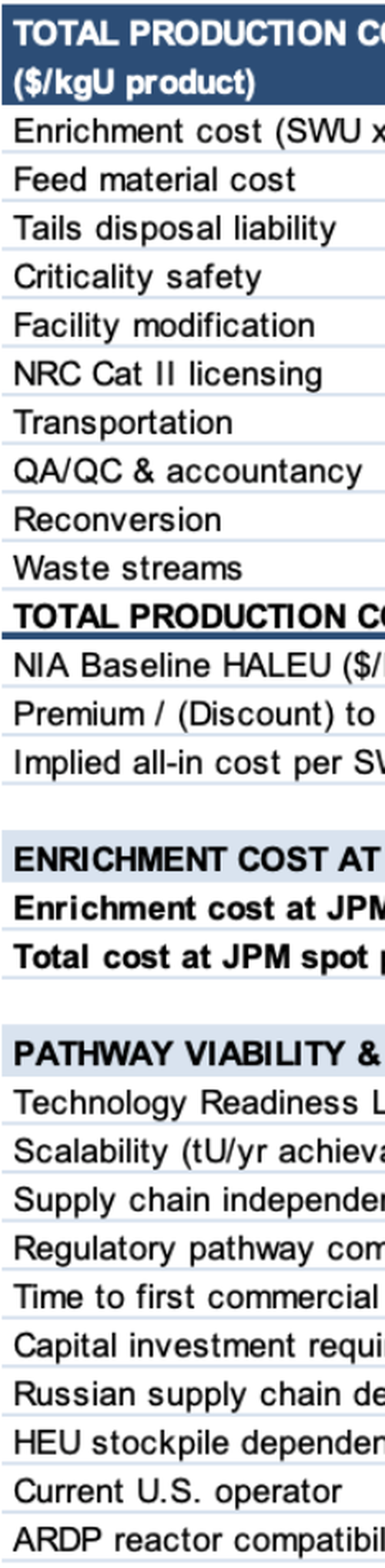
- Comprehensive Enrichment Cost Parameter Framework Assumptions Explained
- SWU Physics & Material Balance
- Regulatory, Licensing & Security
- Feed Material & Conversion Costs
- Tails Management & Disposal Pathways
- & Modeling 9 different enrichment pathways